02 THYROID
02 THYROID
13 02 THYROID
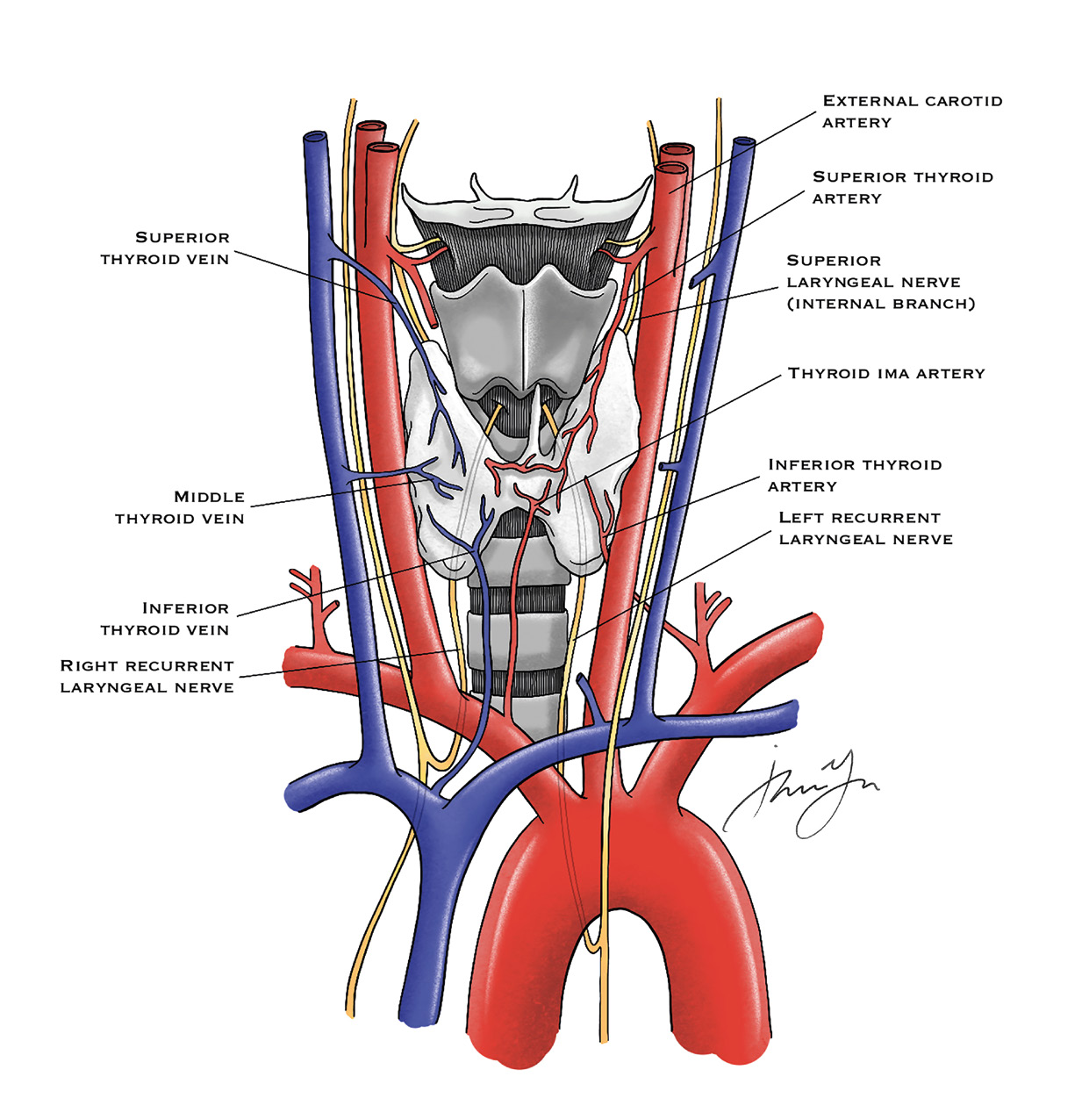
14 02 THYROID High Yield Anatomy Figure 1: Thyroid Anatomy (Thyroid in Grey) Vascular supply: • Superior thyroid artery: branch from External carotid artery • Inferior thyroid artery: branch off of thyrocervical artery • Ima artery off of innominate directly to the isthmus • Superior thyroid vein drains into IJV, inferior drains into innominate vein Nerves: • Superior laryngeal nerve: motor to cricothyroid muscle; loss of projection and fatigue • Recurrent laryngeal nerve: Right travels with vagus and loops around Right innominate artery
15 02 THYROID • Left travels with vagus and loops around aorta • Preoperative laryngoscopy to visualize cords, bilateral damage can obstruct airway Thyroglobulin: stores T3 (more active) and T4 Thyroid Embryology: 4th Endodermal pouch Bilobed solid organ—follicular cells, colloid and parafollicular cells (produces calcitonin) Pyramidal lobe extension can cause thyroglossal duct cyst; resect this as it has the potential to get infected or malignant transformation High-Yield Pathophysiology/Treatment • Thyroid storm: o Seen in Grave’s disease o Treatment with beta blockers, Lugol’s solution, cooling blankets • Thyroid Nodule: o Ultrasound (Look for hypoechogenecity, microcalcification, irregular margins, unorganized vascular patterns, lymphatic invasion) followed by FNA • Indeterminant • Repeat FNA • Benign • Repeat US in 6-12 months • AUS/FLUS • Repeat FNA • Follicular neoplasm • Lobectomy • Suspicious malignancy • Lobectomy • Malignancy • Total thyroidectomy Table 1: Bethesda Criteria *AUS – Atypia of undetermined significance **FLUS – Follicular lesion of undetermined significance
16
02 THYROID
• Hyperthyroidism:
o Low TSH, elevated T3, T4
o Treatment with PTU (side effects of aplastic anemia or
agranulocytosis) or methimazole (cretinism, aplastic anemia
and agranulocytosis)
o PTU OK during Pregnancy as it does not cross placenta
• Graves’ disease:
o Diffuse uptake of radioactive iodine (RAI), antibodies against
TSH receptors
o RAI worsens ophthalmopathy
• Multi-nodular goiter:
o Total or subtotal thyroidectomy
• Thyroiditis:
o Hashimoto’s: caused by antithyroid antibodies; treatment
with thyroid replacement
o Subacute granulomatous: viral etiology, treatment with
NSAIDs, steroids
• Papillary thyroid cancer:
o MC thyroid malignancy; in women; spread lymphatically
o Biopsy pathology shows psammoma bodies, orphan Annie
nucleus
o Tx with total thyroidectomy with Level VI involvement
• Do total – so can follow up thyroglobulin for surveillance,
postoperative radioiodine treatment, remove potential
multifocal disease
• Follicular Thyroid Cancer:
o FNA is not reliable so do diagnostic/therapeutic lobectomy
o Hematogenous spread
o Treatment with total thyroidectomy, MRND for + nodes and
postoperative Radioactive iodine ablation
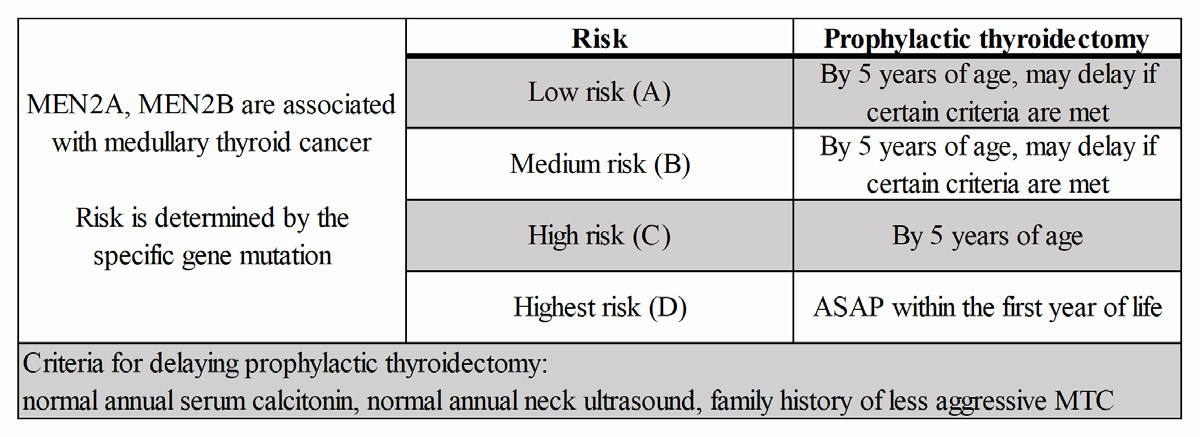
17 02 THYROID • Medullary Thyroid Cancer: o Cancer from parafollicular C cells producing Calcitonin o 20% associated with germline mutations in RET oncogene o Tx with total thyroidectomy with Central dissection, modified radical dissection if lymph nodes involved o Surveillance with CEA, Calcitonin Table 2: MEN and Medullary Thyroid Cancer Quick Hits o Radioactive Iodine ablation does not work for MTC o Avoid injuring the Superior Laryngeal Nerve by ligation close to the superior pole of the thyroid o MC symptom of elevated calcitonin is diarrhea
18 02 THYROID
Figures